
Beginning HTML and CSS
Class 2
Welcome!
Girl Develop It is here to provide affordable and accessible programs to learn software through mentorship and hands-on instruction.
Some "rules"
- We are here for you!
- Every question is important
- Help each other
- Have fun
Anatomy of a website
A website is a way to present your content to the world, using HTML and CSS to present that content & make it look good.
CSS: What is it?
CSS = Cascading Style Sheets
CSS is a "style sheet language" that lets you style the elements on your page.
CSS is works in conjunction with HTML, but is not HTML itself.
CSS: What can it do?
All colored text, position, and size
CSS: What does it look like?

The CSS Rule
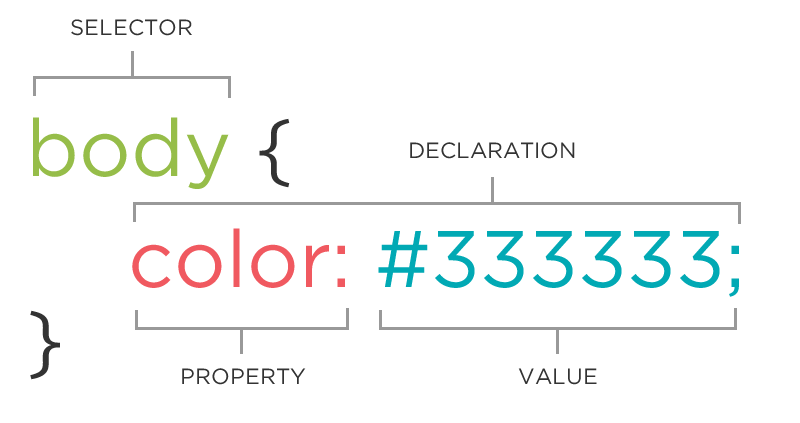
The CSS Rule
selector {
property: value;
}
A block of CSS code is a rule.
The rule starts with a selector.
It has sets of properties and values.
A property-value pair is a declaration.
CSS Syntax
Declarations: Property and value of style you plan use on HTML element.
Declarations end with a semicolon
Declaration groups are surrounded by curly brackets.
selector {
property: value;
property: value;
property: value;
}
Selector: Element
p {
property: value;
}
Selects all paragraph elements.
img {
property: value;
}
Selects all image elements.
Property Values
Each property can have one or more comma separated values.
p{
color: white;
background-color: red;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}
Property: Color
The color property changes the color of the text.
p {
color: red;
color: #ff0000;
color: rgb(255, 0, 0);
}
Any of these will turn the text of this paragraph red.
Property: Background-color
The background-color property changes the color of the background.
p {
background-color: black;
background-color: #000000;
background-color: rgb(0,0,0);
}
Color Values
We have several ways of representing color. These are all the same blue:
p {
color: blue;
color: #0000ff;
color: rgb(0, 0, 255);
}
Color names
Some basic color name examples: aqua, black, blue, fuchsia, gray, grey, green, lime, maroon, navy, olive, purple, red, silver, teal, white, and yellow.
(And there are lots more!)
Hexadecimal and RGB values
Represent the amount of Red, Green, and Blue in a color, from 0 to a maximum of 255 or FF.
Connecting CSS to HTML
3 ways
"Inline"
"Embedded"
"External"
Connecting CSS to HTML: Inline
<p style="color:red">Some text.</p>
Uses the HTML attribute style.
Difficult to use in large projects
Not preferred.
Connecting CSS to HTML: Embedded
<head>
<style type="text/css">
p {
color: blue;
font-size: 12px;
}
</style>
</head>
Inside <head> element.
Uses <style> tag.
Can only be used in one html file
Connecting CSS to HTML: Linked
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css">
</head>
Shared resource for several pages.
Reduced file size & bandwidth
Easy to maintain in larger projects.
Preferred by nerds everywhere!
Let's develop it
- Create a new .css file
- Add a link to the file in the head of the portfolio made last time
- Add styles to change the colors and background colors your elements
Property: Font-family
The font-family property defines which font is used.
p {
font-family: "Times New Roman";
font-family: serif;
font-family: Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
}
Specific font name
Generic name
Comma-separated list
Property: Font-size
The font-size property specifies the size of the font.
p {
font-size: 12px;
font-size: 1.5em;
font-size: 100%;
}
Pixels
"em"
Percentage
Property: Font (shorthand)
p {
font-style: italic;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 10px;
font-family: sans-serif;
}
p {
font: italic bold 10px sans-serif;
}
Property: Line-height
The line-height property specifies the amount of space each line of type takes up.
p {
line-height: 18px;
line-height: 1.5em;
line-height: 150%;
line-height: 1.5;
}
Note: Line-height includes the height of the type! If your line-height is smaller than your font-size, you will get overlapping lines.
Property: Text-transform
The text-transform property allows you to override the capitalization of an entire block of text, regardless of how the text was actually entered.
h2 {
text-transform: uppercase;
text-transform: lowercase;
text-transform: capitalize;
}
Let's develop it
- Adjust the type on your page using font, line-height, and text-transform properties
- You can style paragraphs, headers (h1 - h6), and lists
Selector: ID
#footer {
property: value;
}
Selects all elements with an id of "footer".
<p id="footer">Copyright 2011</p>
The associated HTML.
Selector: Class
.warning {
color: red;
}
Selects all elements with a class of "warning".
<p class="warning">Run away!</p>
The associated HTML.
IDs vs. Classes
The "#" is how you tell CSS "this is an id."
The "." is how you tell CSS "this is a class name."
Selector: Position
p em {
color: yellow;
}
Selects all em elements that are within a paragraph
<p>This is <em>important.</em></p>
This is important.
Cascading
Styles "cascade" down until changed
p{
color: blue;
font-family: 'Helvetica';
}
.red{
color: red;
}
#special{
font-family: Arial;
}
<p>Paragraph</p>
<p class="green">Paragraph</p>
<p class="red">Paragraph</p>
<p class="red" id="special">Paragraph</p>
CSS Properties
Many CSS properties have self-explanatory names:
- background-color
- font-family
- font-size
- color
- width
- height
Let's develop it
- Use Classes and IDs to override the styles of some elements but not others (don't forget the HTML!)
- Try out at least one new property that we didn't cover in today's slides.